使用代理
🌐 Using Agents
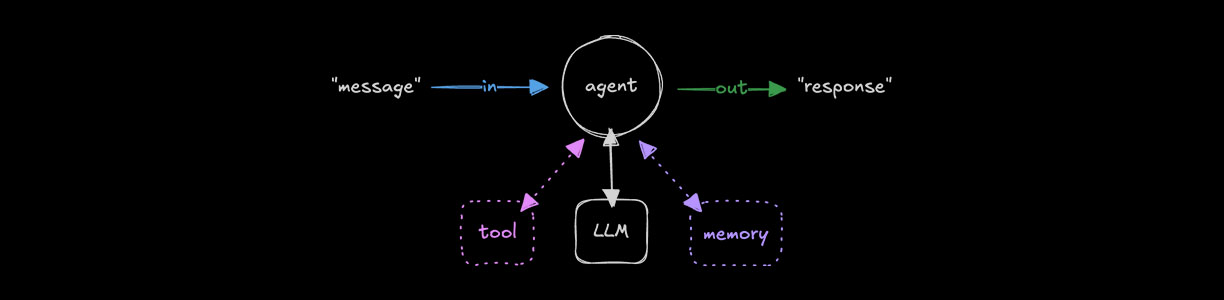
智能体使用大语言模型和工具来解决开放性任务。它们会对目标进行推断,决定使用哪些工具,保留对话内存,并在内部迭代,直到模型输出最终答案或达到可选的停止条件。智能体会生成结构化响应,你可以在界面中呈现这些响应或以程序化方式处理它们。可以直接使用智能体,也可以将它们组合成工作流或智能体网络。
🌐 Agents use LLMs and tools to solve open-ended tasks. They reason about goals, decide which tools to use, retain conversation memory, and iterate internally until the model emits a final answer or an optional stop condition is met. Agents produce structured responses you can render in your UI or process programmatically. Use agents directly or compose them into workflows or agent networks.
代理介绍,以及它们与工作流程的比较 YouTube(7分钟)
🌐 An introduction to agents, and how they compare to workflows on YouTube (7 minutes)
设置代理Direct link to 设置代理
🌐 Setting up agents
安装Direct link to 安装
🌐 Installation
将 Mastra 核心包添加到你的项目中:
🌐 Add the Mastra core package to your project:
- npm
- pnpm
- Yarn
- Bun
npm install @mastra/core@latestpnpm add @mastra/core@latestyarn add @mastra/core@latestbun add @mastra/core@latestMastra 的模型路由会自动检测你所选提供商的环境变量。对于 OpenAI,请设置
OPENAI_API_KEY:🌐 Mastra's model router auto-detects environment variables for your chosen provider. For OpenAI, set
OPENAI_API_KEY:.envOPENAI_API_KEY=<your-api-key>通过使用系统
instructions和model实例化Agent类来创建代理:🌐 Create an agent by instantiating the
Agentclass with systeminstructionsand amodel:src/mastra/agents/test-agent.tsimport { Agent } from "@mastra/core/agent";
export const testAgent = new Agent({
id: "test-agent",
name: "Test Agent",
instructions: "You are a helpful assistant.",
model: "openai/gpt-5.1",
});
指令格式Direct link to 指令格式
🌐 Instruction formats
指令定义了代理的行为、个性和能力。它们是系统级提示,用于确立代理的核心身份和专业字段。
🌐 Instructions define the agent's behavior, personality, and capabilities. They are system-level prompts that establish the agent's core identity and expertise.
说明可以以多种格式提供,以提高灵活性。下面的示例展示了支持的格式:
🌐 Instructions can be provided in multiple formats for greater flexibility. The examples below illustrate the supported shapes:
// String (most common)
instructions: "You are a helpful assistant.";
// Array of strings
instructions: [
"You are a helpful assistant.",
"Always be polite.",
"Provide detailed answers.",
];
// Array of system messages
instructions: [
{ role: "system", content: "You are a helpful assistant." },
{ role: "system", content: "You have expertise in TypeScript." },
];
特定于提供商的选项Direct link to 特定于提供商的选项
🌐 Provider-specific options
每个模型提供商还提供一些不同的选项,包括提示缓存和推断配置。我们提供了一个 providerOptions 标志来管理这些。你可以在指令层级设置 providerOptions,以便为每个系统指令/提示设置不同的缓存策略。
🌐 Each model provider also enables a few different options, including prompt caching and configuring reasoning. We provide a providerOptions flag to manage these. You can set providerOptions on the instruction level to set different caching strategy per system instruction/prompt.
// With provider-specific options (e.g., caching, reasoning)
instructions: {
role: "system",
content:
"You are an expert code reviewer. Analyze code for bugs, performance issues, and best practices.",
providerOptions: {
openai: { reasoningEffort: "high" }, // OpenAI's reasoning models
anthropic: { cacheControl: { type: "ephemeral" } } // Anthropic's prompt caching
}
}
请访问 代理参考 以获取更多信息。
🌐 Visit Agent reference for more information.
动态指令Direct link to 动态指令
🌐 Dynamic instructions
指令可以作为异步函数提供,使你能够在运行时解析提示。这使得可以实现根据用户上下文个性化指令、从外部注册服务获取提示以及使用不同变体运行 A/B 测试等模式。
🌐 Instructions can be provided as an async function, allowing you to resolve prompts at runtime. This enables patterns like personalizing instructions based on user context, fetching prompts from external registry services, and running A/B tests with different variants.
请参阅 动态说明 以获取示例。
🌐 See Dynamic instructions for examples.
注册代理Direct link to 注册代理
🌐 Registering an agent
在 Mastra 实例中注册你的代理,使其可在整个应用中使用。注册后,它可以从工作流、工具或其他代理中调用,并且可以访问共享资源,如内存、日志记录和可观察性功能:
🌐 Register your agent in the Mastra instance to make it available throughout your application. Once registered, it can be called from workflows, tools, or other agents, and has access to shared resources such as memory, logging, and observability features:
import { Mastra } from "@mastra/core";
import { testAgent } from "./agents/test-agent";
export const mastra = new Mastra({
agents: { testAgent },
});
引用代理Direct link to 引用代理
🌐 Referencing an agent
你可以从工作流步骤、工具、Mastra 客户端或命令行调用代理。根据你的设置,通过在你的 mastra 或 mastraClient 实例上调用 .getAgent() 来获取引用:
🌐 You can call agents from workflow steps, tools, the Mastra Client, or the command line. Get a reference by calling .getAgent() on your mastra or mastraClient instance, depending on your setup:
const testAgent = mastra.getAgent("testAgent");
mastra.getAgent() 优于直接导入,因为它可以访问 Mastra 实例配置(日志记录、遥测、存储、已注册的代理和向量存储)。
生成回应Direct link to 生成回应
🌐 Generating responses
代理可以通过两种方式返回结果:在返回前生成完整输出,或实时流式传输令牌。选择适合你使用场景的方法:对于简短的内部响应或调试,使用生成方式;为了尽快向终端用户传递内容,则使用流式方式。
🌐 Agents can return results in two ways: generating the full output before returning it or streaming tokens in real time. Choose the approach that fits your use case: generate for short, internal responses or debugging, and stream to deliver pixels to end users as quickly as possible.
- Generate
- Stream
对于简单提示,传递一个字符串;当提供多个上下文时,传递一个字符串数组;或者传递包含 role 和 content 的消息对象数组。
(role 定义了每条消息的发言者。典型角色包括 user 表示人类输入,assistant 表示代理响应,system 表示指令。)
const response = await testAgent.generate([
{ role: "user", content: "Help me organize my day" },
{ role: "user", content: "My day starts at 9am and finishes at 5.30pm" },
{ role: "user", content: "I take lunch between 12:30 and 13:30" },
{
role: "user",
content: "I have meetings Monday to Friday between 10:30 and 11:30",
},
]);
console.log(response.text);
对于简单提示,传递一个字符串;当提供多个上下文时,传递一个字符串数组;或者传递包含 role 和 content 的消息对象数组。
(role 定义了每条消息的发言者。典型角色包括 user 表示人类输入,assistant 表示代理响应,system 表示指令。)
const stream = await testAgent.stream([
{ role: "user", content: "Help me organize my day" },
{ role: "user", content: "My day starts at 9am and finishes at 5.30pm" },
{ role: "user", content: "I take lunch between 12:30 and 13:30" },
{
role: "user",
content: "I have meetings Monday to Friday between 10:30 and 11:30",
},
]);
for await (const chunk of stream.textStream) {
process.stdout.write(chunk);
}
使用 onFinish() 完成
在流式返回响应时,onFinish() 回调会在大型语言模型生成响应以及所有工具执行完成后运行。它提供最终的 text、执行 steps、finishReason、令牌 usage 统计信息,以及其他用于监控或记录的元数据。
🌐 When streaming responses, the onFinish() callback runs after the LLM finishes generating its response and all tool executions are complete.
It provides the final text, execution steps, finishReason, token usage statistics, and other metadata useful for monitoring or logging.
const stream = await testAgent.stream("Help me organize my day", {
onFinish: ({ steps, text, finishReason, usage }) => {
console.log({ steps, text, finishReason, usage });
},
});
for await (const chunk of stream.textStream) {
process.stdout.write(chunk);
}
访问 .generate() 或 .stream() 获取更多信息。
🌐 Visit .generate() or .stream() for more information.
结构化输出Direct link to 结构化输出
🌐 Structured output
代理可以使用 Zod 或 JSON Schema 返回结构化、类型安全的数据。解析结果可以在 response.object 上获取。
🌐 Agents can return structured, type-safe data using Zod or JSON Schema. The parsed result is available on response.object.
访问 Structured Output 了解更多信息。
🌐 Visit Structured Output for more information.
分析图片Direct link to 分析图片
🌐 Analyzing images
代理可以通过处理图片的视觉内容以及其中的任何文本来分析和描述图片。要启用图片分析,请在 content 数组中传入包含 type: 'image' 和图片 URL 的对象。你可以将图片内容与文本提示结合起来,以引导代理的分析。
🌐 Agents can analyze and describe images by processing both the visual content and any text within them. To enable image analysis, pass an object with type: 'image' and the image URL in the content array. You can combine image content with text prompts to guide the agent's analysis.
const response = await testAgent.generate([
{
role: "user",
content: [
{
type: "image",
image: "https://placebear.com/cache/395-205.jpg",
mimeType: "image/jpeg",
},
{
type: "text",
text: "Describe the image in detail, and extract all the text in the image.",
},
],
},
]);
console.log(response.text);
使用 maxStepsDirect link to using-maxsteps
🌐 Using maxSteps
maxSteps 参数控制代理可以进行的连续 LLM 调用的最大次数。每个步骤包括生成响应、执行任何工具调用以及处理结果。限制步骤有助于防止无限循环、减少延迟,并控制使用工具的代理的令牌使用量。默认值为 1,但可以增加:
🌐 The maxSteps parameter controls the maximum number of sequential LLM calls an agent can make. Each step includes generating a response, executing any tool calls, and processing the result. Limiting steps helps prevent infinite loops, reduce latency, and control token usage for agents that use tools. The default is 1, but can be increased:
const response = await testAgent.generate("Help me organize my day", {
maxSteps: 10,
});
console.log(response.text);
使用 onStepFinishDirect link to using-onstepfinish
🌐 Using onStepFinish
你可以使用 onStepFinish 回调来监控多步骤操作的进度。这对于调试或向用户提供进度更新非常有用。
🌐 You can monitor the progress of multi-step operations using the onStepFinish callback. This is useful for debugging or providing progress updates to users.
onStepFinish 仅在流式传输或生成非结构化输出文本时可用。
const response = await testAgent.generate("Help me organize my day", {
onStepFinish: ({ text, toolCalls, toolResults, finishReason, usage }) => {
console.log({ text, toolCalls, toolResults, finishReason, usage });
},
});
使用工具Direct link to 使用工具
🌐 Using tools
代理可以使用工具来超越语言生成,实现与外部 API 和服务的结构化交互。工具允许代理以可靠、可重复的方式访问数据并执行明确定义的操作。
🌐 Agents can use tools to go beyond language generation, enabling structured interactions with external APIs and services. Tools allow agents to access data and perform clearly defined operations in a reliable, repeatable way.
export const testAgent = new Agent({
id: "test-agent",
name: "Test Agent",
tools: { testTool },
});
访问 使用工具 了解更多信息。
🌐 Visit Using Tools for more information.
使用 RequestContextDirect link to using-requestcontext
🌐 Using RequestContext
使用 RequestContext 来访问请求特定的值。这可以让你根据请求的上下文有条件地调整行为。
🌐 Use RequestContext to access request-specific values. This lets you conditionally adjust behavior based on the context of the request.
export type UserTier = {
"user-tier": "enterprise" | "pro";
};
export const testAgent = new Agent({
id: "test-agent",
name: "Test Agent",
model: ({ requestContext }) => {
const userTier = requestContext.get("user-tier") as UserTier["user-tier"];
return userTier === "enterprise"
? "openai/gpt-5"
: "openai/gpt-4.1-nano";
},
});
有关更多信息,请参见 请求上下文。
🌐 See Request Context for more information.
使用 Studio 进行测试Direct link to 使用 Studio 进行测试
🌐 Testing with Studio
使用 Studio 来测试带有不同消息的代理,检查工具调用和响应,并调试代理行为。
🌐 Use Studio to test agents with different messages, inspect tool calls and responses, and debug agent behavior.
相关Direct link to 相关
🌐 Related