人机交互循环(HITL)
🌐 Human-in-the-loop (HITL)
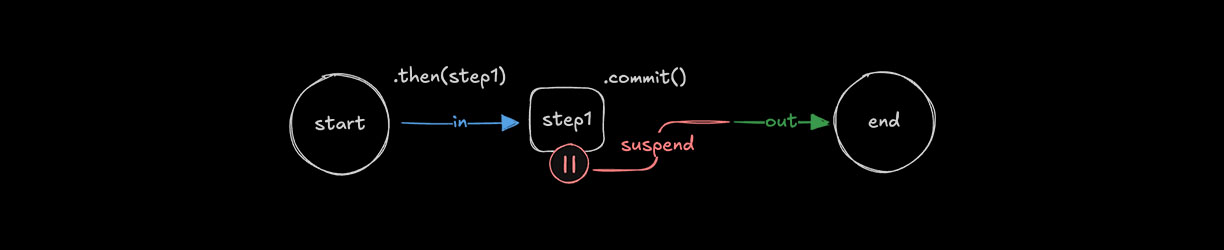
有些工作流程需要在继续之前暂停以等待人工输入。当工作流程被suspended时,它可以返回一条消息,说明暂停的原因以及继续所需的操作。然后,工作流程可以根据收到的输入选择resume继续或bail退出。这种方法适用于手动审批、拒绝、受控决策或任何需要人工监督的步骤。
🌐 Some workflows need to pause for human input before continuing. When a workflow is suspended, it can return a message explaining why it paused and what’s needed to proceed. The workflow can then either resume or bail based on the input received. This approach works well for manual approvals, rejections, gated decisions, or any step that requires human oversight.
暂停工作流以进行人工输入Direct link to 暂停工作流以进行人工输入
🌐 Pausing workflows for human input
人机交互输入的工作方式很像使用 suspend() 暂停工作流。关键区别在于,当需要人工输入时,你可以使用 suspend() 返回一个负载,为用户提供继续操作的上下文或指导。
🌐 Human-in-the-loop input works much like pausing a workflow using suspend(). The key difference is that when human input is required, you can return suspend() with a payload that provides context or guidance to the user on how to continue.
import { createWorkflow, createStep } from "@mastra/core/workflows";
import { z } from "zod";
const step1 = createStep({
id: "step-1",
inputSchema: z.object({
userEmail: z.string()
}),
outputSchema: z.object({
output: z.string()
}),
resumeSchema: z.object({
approved: z.boolean()
}),
suspendSchema: z.object({
reason: z.string()
}),
execute: async ({ inputData, resumeData, suspend }) => {
const { userEmail } = inputData;
const { approved } = resumeData ?? {};
if (!approved) {
return await suspend({
reason: "Human approval required."
});
}
return {
output: `Email sent to ${userEmail}`
};
}
});
export const testWorkflow = createWorkflow({
id: "test-workflow",
inputSchema: z.object({
userEmail: z.string()
}),
outputSchema: z.object({
output: z.string()
})
})
.then(step1)
.commit();
提供用户反馈Direct link to 提供用户反馈
🌐 Providing user feedback
当工作流被暂停时,你可以通过识别被暂停的步骤并读取其 suspendPayload 来访问 suspend() 返回的有效负载。
🌐 When a workflow is suspended, you can access the payload returned by suspend() by identifying the suspended step and reading its suspendPayload.
const workflow = mastra.getWorkflow("testWorkflow");
const run = await workflow.createRun();
const result = await run.start({
inputData: {
userEmail: "alex@example.com"
}
});
if (result.status === "suspended") {
const suspendStep = result.suspended[0];
const suspendedPayload = result.steps[suspendStep[0]].suspendPayload;
console.log(suspendedPayload);
}
Example output
该步骤返回的数据可以包含原因,并帮助用户了解恢复工作流程所需的内容。
🌐 The data returned by the step can include a reason and help the user understand what’s needed to resume the workflow.
{ reason: 'Confirm to send email.' }
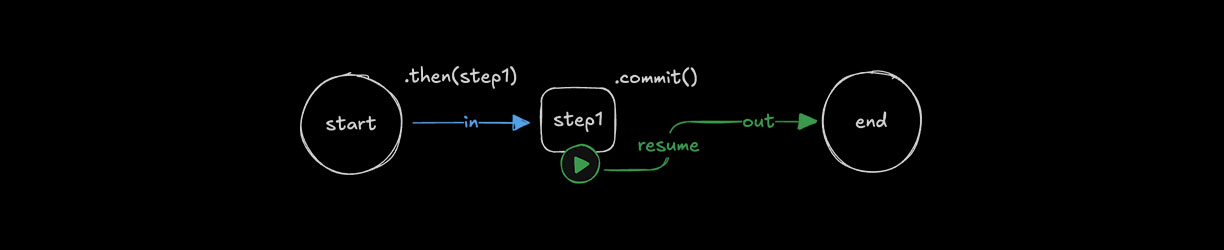
在有人为输入的情况下恢复工作流程Direct link to 在有人为输入的情况下恢复工作流程
🌐 Resuming workflows with human input
与重新启动工作流一样,在从人类接收输入后,使用 resume() 和 resumeData 来继续工作流。工作流将从暂停的步骤处恢复。
🌐 As with restarting a workflow, use resume() with resumeData to continue a workflow after receiving input from a human. The workflow resumes from the step where it was paused.
const workflow = mastra.getWorkflow("testWorkflow");
const run = await workflow.createRun();
await run.start({
inputData: {
userEmail: "alex@example.com"
}
});
const handleResume = async () => {
const result = await run.resume({
step: "step-1",
resumeData: { approved: true }
});
};
用 bail() 处理人类的拒绝Direct link to handling-human-rejection-with-bail
🌐 Handling human rejection with bail()
使用 bail() 可以在一个步骤中停止工作流执行而不触发错误。当人为明确拒绝某个操作时,这非常有用。工作流将以 success 状态完成,并且在调用 bail() 之后的任何逻辑都会被跳过。
🌐 Use bail() to stop workflow execution at a step without triggering an error. This can be useful when a human explicitly rejects an action. The workflow completes with a success status, and any logic after the call to bail() is skipped.
const step1 = createStep({
execute: async ({ inputData, resumeData, suspend, bail }) => {
const { userEmail } = inputData;
const { approved } = resumeData ?? {};
if (approved === false) {
return bail({
reason: "User rejected the request."
});
}
if (!approved) {
return await suspend({
reason: "Human approval required."
});
}
return {
message: `Email sent to ${userEmail}`
};
}
});
多轮人类输入Direct link to 多轮人类输入
🌐 Multi-turn human input
对于需要在多个阶段输入的工作流,暂停模式保持不变。每个步骤都会定义一个 resumeSchema,以及通常带有原因的 suspendSchema,这些原因可用于向用户提供反馈。
🌐 For workflows that require input at multiple stages, the suspend pattern remains the same. Each step defines a resumeSchema, and suspendSchema typically with a reason that can be used to provide user feedback.
const step1 = createStep({...});
const step2 = createStep({
id: "step-2",
inputSchema: z.object({
message: z.string()
}),
outputSchema: z.object({
output: z.string()
}),
resumeSchema: z.object({
approved: z.boolean()
}),
suspendSchema: z.object({
reason: z.string()
}),
execute: async ({ inputData, resumeData, suspend }) => {
const { message } = inputData;
const { approved } = resumeData ?? {};
if (!approved) {
return await suspend({
reason: "Human approval required."
});
}
return {
output: `${message} - Deleted`
};
}
});
export const testWorkflow = createWorkflow({
id: "test-workflow",
inputSchema: z.object({
userEmail: z.string()
}),
outputSchema: z.object({
output: z.string()
})
})
.then(step1)
.then(step2)
.commit();
每一步都必须按顺序恢复,对每个暂停的步骤都需单独调用 resume()。这种方法有助于在多步骤审批中管理过程,确保每个阶段都有一致的界面反馈和清晰的输入处理。
🌐 Each step must be resumed in sequence, with a separate call to resume() for each suspended step. This approach helps manage multi-step approvals with consistent UI feedback and clear input handling at each stage.
const handleResume = async () => {
const result = await run.resume({
step: "step-1",
resumeData: { approved: true }
});
};
const handleDelete = async () => {
const result = await run.resume({
step: "step-2",
resumeData: { approved: true }
});
};
相关Direct link to 相关
🌐 Related