工作流程概览
🌐 Workflows overview
工作流让你可以使用清晰的、结构化的步骤来定义复杂的任务序列,而不是依赖单个代理的推断。它们让你完全控制任务如何被分解、数据如何在任务之间流动以及何时执行。工作流默认使用内置执行引擎运行,也可以部署到像 Inngest 这样的工作流运行器上,以实现托管基础设施。
🌐 Workflows let you define complex sequences of tasks using clear, structured steps rather than relying on the reasoning of a single agent. They give you full control over how tasks are broken down, how data moves between them, and what gets executed when. Workflows run using the built-in execution engine by default, or can be deployed to workflow runners like Inngest for managed infrastructure.
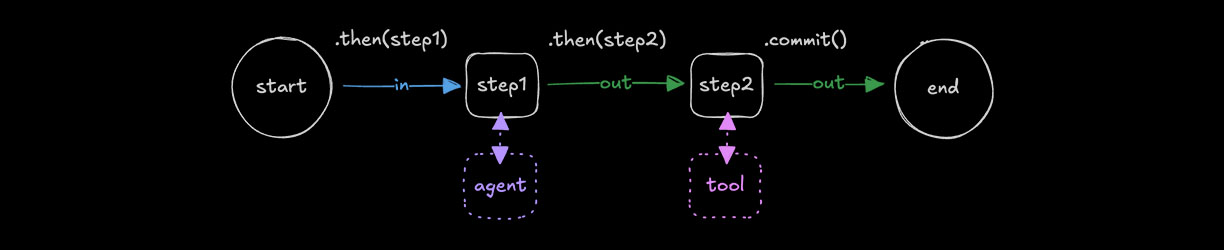
何时使用工作流Direct link to 何时使用工作流
🌐 When to use workflows
将工作流用于那些事先明确定义、并且涉及多个按特定执行顺序执行的步骤的任务。它们可以让你对数据在各个步骤之间的流动和转换,以及每个阶段调用哪些基本操作,有精细的控制。
🌐 Use workflows for tasks that are clearly defined upfront and involve multiple steps with a specific execution order. They give you fine-grained control over how data flows and transforms between steps, and which primitives are called at each stage.
📹 观看:→ 工作流程简介,以及它们与代理的比较 YouTube(7 分钟)
核心原则Direct link to 核心原则
🌐 Core principles
Mastra 工作流程的运行基于以下原则:
🌐 Mastra workflows operate using these principles:
- 使用
createStep定义 步骤,指定输入/输出模式和业务逻辑。 - 使用
createWorkflow组合步骤以定义执行流程。 - 运行工作流以执行整个序列,内置支持暂停、恢复和流式结果。
创建工作流步骤Direct link to 创建工作流步骤
🌐 Creating a workflow step
步骤是工作流的构建模块。使用 createStep() 创建一个步骤,并通过 inputSchema 和 outputSchema 定义它接受和返回的数据。
🌐 Steps are the building blocks of workflows. Create a step using createStep() with inputSchema and outputSchema to define the data it accepts and returns.
execute 函数定义了这个步骤的功能。使用它来调用你代码库中的函数、外部 API、代理或工具。
🌐 The execute function defines what the step does. Use it to call functions in your codebase, external APIs, agents, or tools.
import { createStep } from "@mastra/core/workflows";
const step1 = createStep({
id: "step-1",
inputSchema: z.object({
message: z.string()
}),
outputSchema: z.object({
formatted: z.string()
}),
execute: async ({ inputData }) => {
const { message } = inputData;
return {
formatted: message.toUpperCase()
};
}
});
访问 Step Class 获取完整的配置选项列表。
🌐 Visit Step Class for a full list of configuration options.
使用代理和工具Direct link to 使用代理和工具
🌐 Using agents and tools
工作流步骤还可以调用已注册的代理或直接导入并执行工具,更多信息请访问使用工具页面。
🌐 Workflow steps can also call registered agents or import and execute tools directly, visit the Using Tools page for more information.
创建工作流程Direct link to 创建工作流程
🌐 Creating a workflow
使用 createWorkflow() 和 inputSchema 及 outputSchema 创建一个工作流,以定义其接受和返回的数据。使用 .then() 添加步骤,并用 .commit() 完成工作流。
🌐 Create a workflow using createWorkflow() with inputSchema and outputSchema to define the data it accepts and returns. Add steps using .then() and complete the workflow with .commit().
import { createWorkflow, createStep } from "@mastra/core/workflows";
import { z } from "zod";
const step1 = createStep({...});
export const testWorkflow = createWorkflow({
id: "test-workflow",
inputSchema: z.object({
message: z.string()
}),
outputSchema: z.object({
output: z.string()
})
})
.then(step1)
.commit();
请访问 Workflow Class 查看完整的配置选项列表。
🌐 Visit Workflow Class for a full list of configuration options.
理解控制流程Direct link to 理解控制流程
🌐 Understanding control flow
工作流可以使用多种不同的方法来组合。你选择的方法决定了每个步骤的模式应如何构建。有关更多信息,请访问 控制流 页面。
🌐 Workflows can be composed using a number of different methods. The method you choose determines how each step's schema should be structured. Visit the Control Flow page for more information.
工作流状态Direct link to 工作流状态
🌐 Workflow state
工作流状态允许你在各个步骤之间共享值,而无需通过每个步骤的 inputSchema 和 outputSchema 传递它们。使用状态来跟踪进度、累计结果或在整个工作流中共享配置。
🌐 Workflow state lets you share values across steps without passing them through every step's inputSchema and outputSchema. Use state for tracking progress, accumulating results, or sharing configuration across the entire workflow.
const step1 = createStep({
id: "step-1",
inputSchema: z.object({ message: z.string() }),
outputSchema: z.object({ formatted: z.string() }),
stateSchema: z.object({ counter: z.number() }),
execute: async ({ inputData, state, setState }) => {
// Read from state
console.log(state.counter);
// Update state for subsequent steps
setState({ ...state, counter: state.counter + 1 });
return { formatted: inputData.message.toUpperCase() };
},
});
访问 Workflow State 获取有关状态架构、初始状态、挂起/恢复期间的持久性以及嵌套工作流的完整文档。
🌐 Visit Workflow State for complete documentation on state schemas, initial state, persistence across suspend/resume, and nested workflows.
工作流程作为步骤Direct link to 工作流程作为步骤
🌐 Workflows as steps
将工作流用作一个步骤,以便在更大的组合中重用其逻辑。输入和输出遵循核心原则中描述的相同模式规则。
🌐 Use a workflow as a step to reuse its logic within a larger composition. Input and output follow the same schema rules described in Core principles.
const step1 = createStep({...});
const step2 = createStep({...});
const childWorkflow = createWorkflow({
id: "child-workflow",
inputSchema: z.object({
message: z.string()
}),
outputSchema: z.object({
emphasized: z.string()
})
})
.then(step1)
.then(step2)
.commit();
export const testWorkflow = createWorkflow({
id: "test-workflow",
inputSchema: z.object({
message: z.string()
}),
outputSchema: z.object({
emphasized: z.string()
})
})
.then(childWorkflow)
.commit();
克隆工作流Direct link to 克隆工作流
🌐 Cloning a workflow
当你想重复使用某个工作流的逻辑但希望在新的 ID 下单独跟踪时,可以使用 cloneWorkflow() 克隆该工作流。每个克隆都是独立运行的,并且在日志和可观察性工具中显示为一个独立的工作流。
🌐 Clone a workflow using cloneWorkflow() when you want to reuse its logic but track it separately under a new ID. Each clone runs independently and appears as a distinct workflow in logs and observability tools.
import { cloneWorkflow } from "@mastra/core/workflows";
const step1 = createStep({...});
const parentWorkflow = createWorkflow({...})
const clonedWorkflow = cloneWorkflow(parentWorkflow, { id: "cloned-workflow" });
export const testWorkflow = createWorkflow({...})
.then(step1)
.then(clonedWorkflow)
.commit();
注册工作流Direct link to 注册工作流
🌐 Registering a workflow
在 Mastra 实例中注册你的工作流,使其在整个应用中可用。注册后,它可以从代理或工具中调用,并且可以访问共享资源,例如日志记录和可观测性功能:
🌐 Register your workflow in the Mastra instance to make it available throughout your application. Once registered, it can be called from agents or tools and has access to shared resources such as logging and observability features:
import { Mastra } from "@mastra/core/mastra";
import { testWorkflow } from "./workflows/test-workflow";
export const mastra = new Mastra({
workflows: { testWorkflow },
});
引用工作流Direct link to 引用工作流
🌐 Referencing a workflow
你可以从代理、工具、Mastra 客户端或命令行运行工作流。根据你的设置,通过在你的 mastra 或 mastraClient 实例上调用 .getWorkflow() 来获取引用:
🌐 You can run workflows from agents, tools, the Mastra Client, or the command line. Get a reference by calling .getWorkflow() on your mastra or mastraClient instance, depending on your setup:
const testWorkflow = mastra.getWorkflow("testWorkflow");
mastra.getWorkflow() is preferred over a direct import for two reasons:
- 它提供对 Mastra 实例配置的访问(日志记录、遥测、存储、已注册代理和向量存储)
- 它为工作流的输入和输出模式提供完整的 TypeScript 类型推断
注意: 使用 getWorkflow() 与工作流的 注册密钥(添加到 Mastra 时使用的密钥)。虽然 getWorkflowById() 可用于通过其 id 属性检索工作流,但它无法提供相同级别的类型推断。
运行工作流Direct link to 运行工作流
🌐 Running workflows
工作流可以以两种模式运行:start 模式会在所有步骤完成后才返回结果,而 stream 模式则会在执行过程中触发事件。根据你的使用场景选择合适的方法:当你只需要最终结果时使用 start,当你希望监控进度或在步骤完成时触发操作时使用 stream。
🌐 Workflows can be run in two modes: start waits for all steps to complete before returning, and stream emits events during execution. Choose the approach that fits your use case: start when you only need the final result, and stream when you want to monitor progress or trigger actions as steps complete.
- Start
- Stream
使用 createRun() 创建一个工作流运行实例,然后使用与工作流的 inputSchema 匹配的 inputData 调用 .start()。工作流执行所有步骤并返回最终结果。
const run = await testWorkflow.createRun();
const result = await run.start({
inputData: {
message: "Hello world"
}
});
if (result.status === "success") {
console.log(result.result);
}
Create a workflow run instance using .createRun(), then call .stream() with inputData matching the workflow's inputSchema. Iterate over fullStream to track progress, then await result to get the final workflow result.
const run = await testWorkflow.createRun();
const stream = run.stream({
inputData: {
message: "Hello world"
}
});
for await (const chunk of stream.fullStream) {
console.log(chunk);
}
// Get the final result (same type as run.start())
const result = await stream.result;
if (result.status === "success") {
console.log(result.result);
}
工作流结果类型Direct link to 工作流结果类型
🌐 Workflow result type
run.start() 和 stream.result 都会基于 status 属性返回一个区分联合类型,该属性可以是 success、failed、suspended、tripwire 或 paused。无论状态如何,你总可以安全访问 result.status、result.input、result.steps,以及可选的 result.state。
🌐 Both run.start() and stream.result return a discriminated union based on the status property, which can be success, failed, suspended, tripwire, or paused. You can always safely access result.status, result.input, result.steps, and optionally result.state regardless of the status.
此外,根据状态的不同,可用的属性也不同:
🌐 Additionally, depending on the status, different properties are available:
| 状态 | 独特属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
success | result | 工作流的输出数据 |
failed | error | 导致失败的错误 |
tripwire | tripwire | 包含 reason、retry?、metadata?、processorId? |
suspended | suspendPayload、suspended | 挂起数据和挂起步骤路径数组 |
paused | (无) | 仅可用通用属性 |
要访问特定状态的属性,请先检查 status:
🌐 To access status-specific properties, check the status first:
const result = await run.start({ inputData: { message: "Hello world" } });
if (result.status === "success") {
console.log(result.result); // Only available when status is "success"
} else if (result.status === "failed") {
console.log(result.error.message);
} else if (result.status === "suspended") {
console.log(result.suspendPayload);
}
工作流输出Direct link to 工作流输出
🌐 Workflow output
这是一个成功工作流程结果的示例,显示了 input、steps 和 result 属性:
🌐 Here's an example of a successful workflow result, showing the input, steps, and result properties:
{
"status": "success",
"steps": {
"step-1": {
"status": "success",
"payload": {
"message": "Hello world"
},
"output": {
"formatted": "HELLO WORLD"
}
},
"step-2": {
"status": "success",
"payload": {
"formatted": "HELLO WORLD"
},
"output": {
"emphasized": "HELLO WORLD!!!"
}
}
},
"input": {
"message": "Hello world"
},
"result": {
"emphasized": "HELLO WORLD!!!"
}
}
正在重新启动活动的工作流运行Direct link to 正在重新启动活动的工作流运行
🌐 Restarting active workflow runs
当工作流运行与服务器失去连接时,可以从最后一个活动步骤重新启动。这对于可能在服务器断开连接时仍在运行的长时间运行的工作流非常有用。重新启动工作流运行将从最后一个活动步骤恢复执行,工作流将从那里继续。
🌐 When a workflow run loses connection to the server, it can be restarted from the last active step. This is useful for long-running workflows that might still be running when the server loses connection. Restarting a workflow run will resume execution from the last active step, and the workflow will continue from there.
重新启动工作流 restartAllActiveWorkflowRuns() 的所有活动工作流运行Direct link to restarting-all-active-workflow-runs-of-a-workflow-with-restartallactiveworkflowruns
🌐 Restarting all active workflow runs of a workflow with restartAllActiveWorkflowRuns()
使用 restartAllActiveWorkflowRuns() 可以重启某个工作流的所有活动运行。这有助于重启工作流的所有活动运行,而无需手动逐个循环并重启每个运行。
🌐 Use restartAllActiveWorkflowRuns() to restart all active workflow runs of a workflow. This helps restart all active workflow runs of a workflow, without having to manually loop through each run and restart.
workflow.restartAllActiveWorkflowRuns();
使用 restart() 重新启动正在运行的工作流Direct link to restarting-an-active-workflow-run-with-restart
🌐 Restarting an active workflow run with restart()
使用 restart() 从上一次活动步骤重新启动一个正在运行的工作流程。这将从上一次活动步骤继续执行,工作流程将从该步骤继续运行。
🌐 Use restart() to restart an active workflow run from the last active step. This will resume execution from the last active step, and the workflow will continue from there.
const run = await workflow.createRun();
const result = await run.start({ inputData: { value: "initial data" } });
const restartedResult = await run.restart();
识别活动的工作流运行Direct link to 识别活动的工作流运行
🌐 Identifying active workflow runs
当工作流运行处于活动状态时,其 status 将是 running 或 waiting。你可以检查工作流的 status 以确认其是否处于活动状态,并使用 active 来识别活动的工作流运行。
🌐 When a workflow run is active, it will have a status of running or waiting. You can check the workflow's status to confirm it's active, and use active to identify the active workflow run.
const activeRuns = await workflow.listActiveWorkflowRuns();
if (activeRuns.runs.length > 0) {
console.log(activeRuns.runs);
}
在运行本地 Mastra 服务器时,所有正在运行的工作流将在服务器启动时自动重新启动。
🌐 When running the local mastra server, all active workflow runs will be restarted automatically when the server starts.
使用 RequestContextDirect link to using-requestcontext
🌐 Using RequestContext
使用 RequestContext 来访问特定请求的值。这使你可以根据请求的上下文有条件地调整行为。
🌐 Use RequestContext to access request-specific values. This lets you conditionally adjust behavior based on the context of the request.
export type UserTier = {
"user-tier": "enterprise" | "pro";
};
const step1 = createStep({
execute: async ({ requestContext }) => {
const userTier = requestContext.get("user-tier") as UserTier["user-tier"];
const maxResults = userTier === "enterprise"
? 1000
: 50;
return { maxResults };
}
});
请访问 Request Context 以获取更多信息。
🌐 Visit Request Context for more information.
使用 Studio 进行测试Direct link to 使用 Studio 进行测试
🌐 Testing with Studio
使用 Studio 可以轻松运行不同输入的工作流,直观查看执行生命周期,查看每个步骤的输入和输出,并更详细地检查工作流的每个部分。
🌐 Use Studio to easily run workflows with different inputs, visualize the execution lifecycle, see the inputs and outputs for each step, and inspect each part of the workflow in more detail.
相关Direct link to 相关
🌐 Related
有关工作流程的详细了解,请参见我们的工作流程指南,其中通过一个实际示例讲解了核心概念。
🌐 For a closer look at workflows, see our Workflow Guide, which walks through the core concepts with a practical example.